
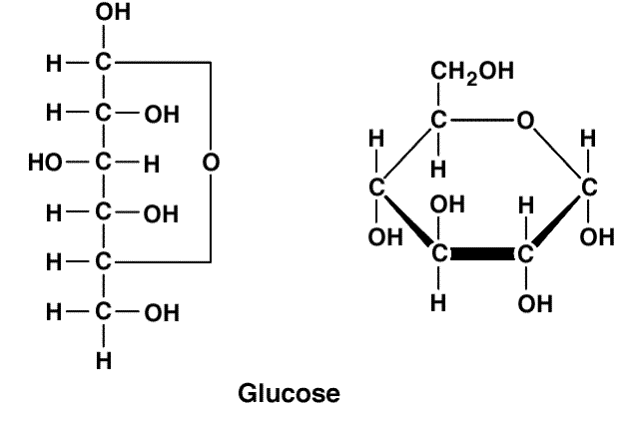
Slow-releasing carbohydrates are long chains of monosaccharides. Carbohydrates are broadly classified into two subgroups, “fast-releasing” and “slow-releasing.” Fast-releasing carbohydrates are further grouped into the monosaccharides and dissacharides. The simplest unit of a carbohydrate is a monosaccharide The simplest unit of a carbohydrate. Synonymous with the term carbohydrate is the Greek word “saccharide,” which means sugar. The chemical formula for glucose is written as C 6H 12O 6. It has six carbon atoms, twelve hydrogen atoms, and six oxygen atoms., the most abundant carbohydrate in the human body, has six carbon atoms, twelve hydrogen atoms, and six oxygen atoms. Glucose The most abundant carbohydrate in the human body. The word “carbo” means carbon and “hydrate” means water. zip file containing this book to use offline, simply click here.Ĭarbohydrates are a group of organic compounds containing a ratio of one carbon atom to two hydrogen atoms to one oxygen atom. You can browse or download additional books there. More information is available on this project's attribution page.įor more information on the source of this book, or why it is available for free, please see the project's home page. Additionally, per the publisher's request, their name has been removed in some passages. However, the publisher has asked for the customary Creative Commons attribution to the original publisher, authors, title, and book URI to be removed. Normally, the author and publisher would be credited here. This content was accessible as of December 29, 2012, and it was downloaded then by Andy Schmitz in an effort to preserve the availability of this book. See the license for more details, but that basically means you can share this book as long as you credit the author (but see below), don't make money from it, and do make it available to everyone else under the same terms. This book is licensed under a Creative Commons by-nc-sa 3.0 license.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
